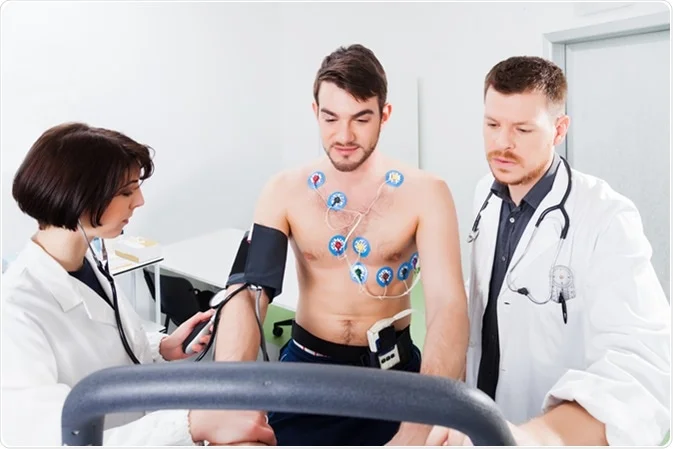
A stress echocardiogram is a medical imaging test that assesses the functioning of the heart by administering a stress test, which induces a stressful environment within the heart. The physician uses ultrasound waves to compare images of the heart before and after the stress test, enabling them to identify any changes or abnormalities that may be occurring. This test is useful in detecting heart problems that may not be visible during a normal echocardiogram.
A stress echocardiogram is a medical test that monitors the blood distribution into the heart, its viability, and its ability to perform its functions. This test is used to diagnose coronary artery disease. There are two types of stress echocardiography procedures, depending on the stimuli used to stress the heart. The physician should decide on the most appropriate method for the patient. The duration of each procedure is usually around 1-2 hours, exclusive of waiting time.
An exercise stress echocardiogram is a medical test where the patient walks on a treadmill with gradually increasing speeds, usually in three-minute intervals. The test stops when the patient becomes exhausted or when the desired exercise level is achieved. On the other hand, a pharmacological stress echocardiogram uses a medication called dobutamine to induce stress on the heart, causing symptoms such as breathlessness or chest pain. Patients may also experience fast and pounding heartbeats after taking the medication.
Preparing for Stress Echocardiography
Because stress echocardiography is uncomfortable, patients are usually advised to do certain preparations before testing. The following are typically advised:
- Eat minimally at least two hours before the test – Patients are usually requested to eat less before the test. While some patients can eat fruit or toast, others are sometimes limited to only water or juice.
- Take necessary medications on time – Ensure that all the physician gives are taken on time unless specified otherwise. It is also advisable to bring a list of current medications for the physician to factor in possible pharmacological contributors or regulators to the heart problem easily.
- Wear comfortable clothing – Because a stress echocardiogram may require physical activity, patients are advised to wear clothing that allows them to move around. Exercising in a hospital setup, patients are usually requested to wear comfortable footwear, jogging pants, and loose shirts.
- Allot at least half a day for the procedure – While a stress echocardiogram usually only takes 1-2 hours, patients are advised to wait, fill out forms, rest, and consult with the physician.